<
Previous
|
Next
|
Contents
>
Difference Equation
Dynamical system come with many different names. Our particular interesting dynamical system is for the system whose state depends on the input history. In discrete time system, we call such system difference equation (equivalent to differential equation in continuous time).
Difference equation is an equation involving differences. We can see difference equation from at least three points of views: as sequence of number, discrete dynamical system and iterated function. It is the same thing but we look at different angle.
- Difference equation is a sequence of numbers that generated recursively using a rule to relate each number in the sequence to previous numbers in the sequence.
Example:
-
Sequence
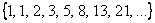 is called Fibonacci sequence, generated with rule
is called Fibonacci sequence, generated with rule
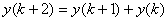 for
for
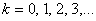 and initial value
and initial value
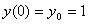
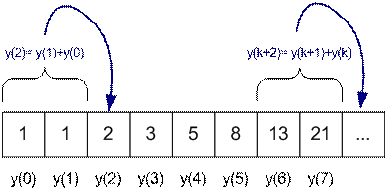
-
Sequence
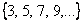 has rule
has rule
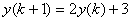 for
for
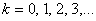 . Both sequences have initial value of
. Both sequences have initial value of
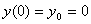 .
.
- Difference equation is a discrete dynamical system that take some discrete input signal and produce output signal
Example:
-
Dynamical system
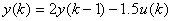 take unit step input
take unit step input
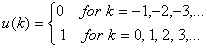 will produce output of
will produce output of
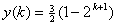

-
Difference equation is an
iterated map
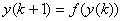 if we see the sequence as an
iterated function
:
if we see the sequence as an
iterated function
:
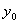 ,
,
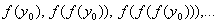 The
The
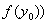 is the first iterate of
is the first iterate of
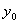 under
under
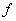 . Notation
. Notation
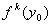 is the k-th iterate of
is the k-th iterate of
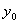 under
under
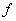 . For example,
. For example,
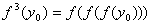 . The set of all iterates of
. The set of all iterates of
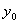 is called the
orbit
of
is called the
orbit
of
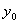 .
.
Example:
Iterated function
![]() for
for
![]() = 1 will produce orbit
= 1 will produce orbit
![]() . If
. If
![]() = 2, the iterated function generate
= 2, the iterated function generate
![]() . When
. When
![]() = 0.5, the iterated function yield sequence of
= 0.5, the iterated function yield sequence of
![]() We see that knowing the rule only is not enough to know the behavior
of the sequence. Initial value is also very important. The orbit of
We see that knowing the rule only is not enough to know the behavior
of the sequence. Initial value is also very important. The orbit of
![]() = 1 is constant for function
= 1 is constant for function
![]() while for
while for
![]() = 2 produces unbounded orbit and the orbit is attracted to zero for
= 2 produces unbounded orbit and the orbit is attracted to zero for
![]() = 0.5. The figure below show the orbit of
= 0.5. The figure below show the orbit of
![]() = 0.5. We will discuss the meaning of this kind of figure later in Phase
Diagram.
= 0.5. We will discuss the meaning of this kind of figure later in Phase
Diagram.

Knowing the initial value and the rule, we can generate
the whole sequence recursively. The value of
![]() is an integer (
is an integer (
![]() ) and the rule to generate the sequence is called the
difference
equation
or the
dynamical system
or
iterated function.
) and the rule to generate the sequence is called the
difference
equation
or the
dynamical system
or
iterated function.
See Also: Index and Initial Value Agreement
<
Previous
|
Next
|
Contents
>
Preferable reference for this tutorial is
Teknomo, Kardi (2015) Difference Equation Tutorial. https:\\people.revoledu.com\kardi\ tutorial\DifferenceEquation\
