<
Previous
|
Next
|
Contents
>
Dynamical System
Dynamical system is a system that changes over time. When we model a system, we usually idealize the system in term of its state variables of the system, which are quantities that represent the system itself. For example, a moving body may be represented by state variable of velocity and position over time. Model of population dynamic, the system state variable may be the number of population that migrate, born and dead and the existing population.
To have better understanding of dynamical system we will contrast dynamical system with the static system. Static system, as you may guess, is a system that does not change over time. The value of variables in the static system is constant. We assume that time is always starts at zero.
Example
Let us begin with simple system as an example:
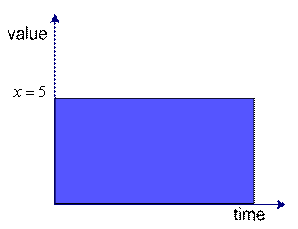
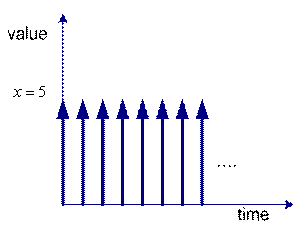
![]() is an example of static system because the value of variable
is an example of static system because the value of variable
![]() is constant over time. We can graph the value of the variable
is constant over time. We can graph the value of the variable
![]() over time. The left figure is the plot for continuous time and the right figure is plot for discrete time. Discrete or continuous time does not matter because it is only our assumption. It is depending on how we view about our problem.
over time. The left figure is the plot for continuous time and the right figure is plot for discrete time. Discrete or continuous time does not matter because it is only our assumption. It is depending on how we view about our problem.
|
|
|
|
Static system in continuous time |
Static system in discrete time |
In contrast, we have
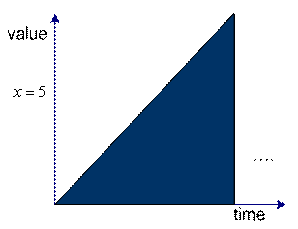
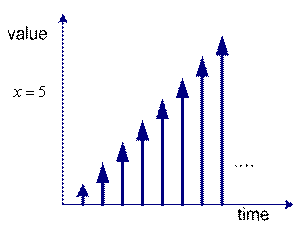
![]() as an example of simple dynamical system. The system is depending on the value of time
as an example of simple dynamical system. The system is depending on the value of time
![]() . We can graph the value of the variable
. We can graph the value of the variable
![]() over time. The left figure is the plot for continuous time and the right figure is plot for discrete time. You may see that the value of the system variable
over time. The left figure is the plot for continuous time and the right figure is plot for discrete time. You may see that the value of the system variable
![]() is changing over time.
is changing over time.
|
|
|
|
Dynamical system in continuous time |
Dynamical system in discrete time |
Superposition
When we do some superposition (add or minus) some static system with a dynamical system, the result is usually will also depend on time. Thus, the superposition of static and dynamical system will also produce dynamical system.
Here is a simple example. We have system that value is given this formula
![]()
You can see easily that this system is actually a combination (or superposition) of two system:
![]() (= a dynamical system) and minus with
(= a dynamical system) and minus with
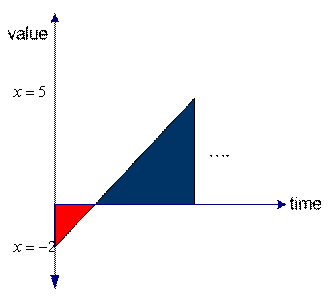
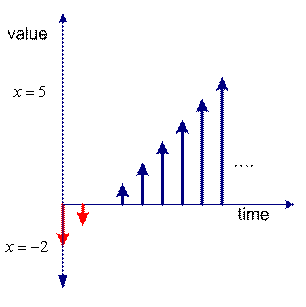
![]() (a static system). The result is changing over time, as shown in the figures below.
(a static system). The result is changing over time, as shown in the figures below.
|
|
|
|
Superposition in continuous time |
Superposition in discrete time |
Whether you want to use discrete or continuous time, it does not matter. Some system is best represented by continuous system, while the others are best to be represented by discrete time. In most cases, system with continuous time has discrete time equivalent.
Why Discrete Dynamical System?
Personally, I prefer discrete time system due to several personal reasons:
- I prefer to use summation (discrete) to integral (continuous) notation because integration makes most of my students afraid. The two are actually equivalent. Similar equivalent can be found between derivative and difference, Laplace transform and Z-transform.
- The sign of discrete time is easily distinguish by arrow, while for continuous time we need color or shading to distinguish positive and negative part (which needs more ink). I prefer the easy plot of discrete time.
- Majority of my students has voted that discrete time system is much easier to understand and to simulate using computer rather than the continuous time.
Thus, from now on we will use discrete time for our dynamical system.
See Also: Index and Initial Value Agreement
<
Previous
|
Next
|
Contents
>
Preferable reference for this tutorial is
Teknomo, Kardi (2015) Difference Equation Tutorial. https:\\people.revoledu.com\kardi\ tutorial\DifferenceEquation\