<
Previous
|
Next
|
Contents
>
Geometric Mean
Geometric mean is n-th root of product of data values.
Formula:
![]()
Property of Geometric Mean
- All data must be positive. Zero data value will produce zero Geometric mean. Negative data value leads to Complex number which commonly regarded as NaN (not a number) in the interactive program below
Example:
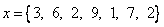
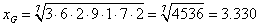
- Geometric mean is scale invariant toward the product of the factor.
For example, we have two objects name A and B, which properties are given below.
Object
Cost ($)
Time (Hour)
A
2
8
B
5
6
Now suppose we would like to make an index based on the two properties of cost and time. We consider geometric mean and arithmetic mean as the index as shown in the table below.
Notice that we are using the same properties; if we change the scale of the time from hour to minutes, arithmetic mean produces rank reversal while geometric index preserve the rank. This is one advantage of geometric mean compare to arithmetic mean
Object GM Index (sqrt($.hour)) AM Index ($+hour) GM Index (sqrt($.min)) AM Index ($+min) A 4 (rank 1) 5 (rank 1) 30.98 (rank 1) 241 (rank 2) B 5.48 (rank 2) 5.5 (rank 2) 42.43(rank 2) 182.5 (rank 1)
The interactive program below computes Geometric mean of a list of numbers separated by comma. Feel free to experiment with your own input values. What happen when you have zero or negative data input? Do you think Geometric mean is robust against outlier or susceptible to error?
<
Previous
|
Next
|
Contents
>
See also:
Lehmer mean
Rate this tutorial or give your comments about this tutorial
