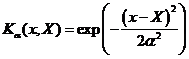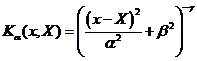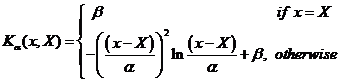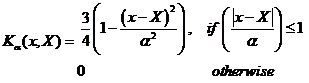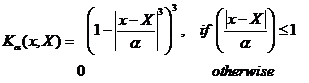<
Previous
|
Next
|
Contents
>
What is Kernel?
Kernel is a kind of bump function that applied to each of data point. We say that the kernel provides a basis function to the regression line. Figure below shows how a kernel of one data point is applied to give weights to the other data points inside the window. Data points outside the window will not be affected by the kernel.
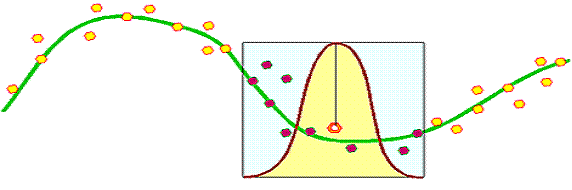
The kernel basis function can be any type of function satisfying the following criteria
- Kernel value is non-negative (can be zero)
-
The maximum value is at the original data point.
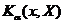 has maximum value when
has maximum value when
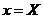
- farther away from the maximum value the kernel value is monotonically decreasing
- In general it is radial symmetric function
We have seen the example of Gaussian function is used for kernel basis function. The following table is list of Kernel basis functions that typically used
|
Kernel Name |
Formula |
Example Plot |
|
Gaussian |
|
|
|
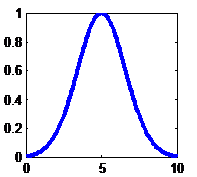
Norm |
|
|
|
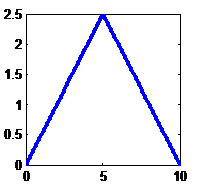
Quadratic |
|
|
|
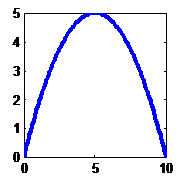
Multi quadratic |
|
|
|
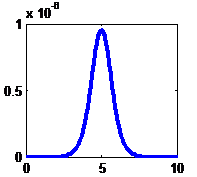
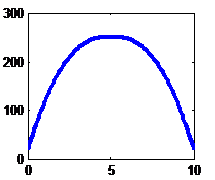
Spline |
|
|
|
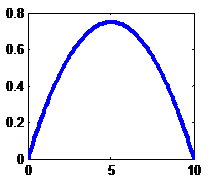
Epanechnikov |
|
|
|
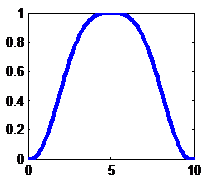
Tri-cube |
|
|
REFERENCES
Vladimir Cherkassky and Filip Mulier (1998) Learning from Data, Concept, Theory and Methods, John Wiley and Sons
Trevor Hastie, Robert Tibshirani, and Jerome Friedman (2001) The element of Statistical Learning, Data Mining, Inference and Prediction, Springer
Note: Matlab code of Kernel Regression can be downloaded from Matlab Central provided by Yi Cao: ksr.m and ksrlin.m
<
Previous
|
Next
|
Contents
>