Generalized Inverse Matrix
Let us recalled how we define the
matrix inverse
. A matrix inverse
![]() is defined as a matrix that produces identity matrix when we multiply with the original matrix
is defined as a matrix that produces identity matrix when we multiply with the original matrix
![]() that is we define
that is we define
![]() .Matrix inverse exists only for
square matrices
.
.Matrix inverse exists only for
square matrices
.
Real world data is not always square. Furthermore, real world data is not always consistent and might contain many repetitions. To deal with real world data, generalized inverse for rectangular matrix is needed.
Generalized inverse matrix is defined as
![]() . Notice that the usual matrix inverse is covered by this definition because
. Notice that the usual matrix inverse is covered by this definition because
![]() . We use term generalized inverse for a general rectangular matrix and to distinguish from inverse matrix that is for a square matrix. Generalized inverse is also called
pseudo inverse
.
. We use term generalized inverse for a general rectangular matrix and to distinguish from inverse matrix that is for a square matrix. Generalized inverse is also called
pseudo inverse
.
Unfortunately there are many types of generalized inverse. Most of generalized inverse are not unique. Some of generalized inverse are reflexive
![]() and some are not reflexive. In this linear algebra tutorial, we will only discuss a few of them that often used in many practical applications.
and some are not reflexive. In this linear algebra tutorial, we will only discuss a few of them that often used in many practical applications.
For example:
-
Reflexive generalized inverse is defined as
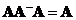
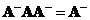
-
Minimum norm generalized inverse such that
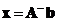 will minimizes
will minimizes
 is defined as
is defined as
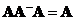
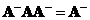
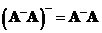
-
Generalized inverse that produces least square solution that will minimize residual or error
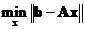 is defined as
is defined as
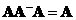
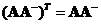
Left Inverse and Right Inverse
The usual matrix inverse is defined as two-sided inverse
![]() because we can multiply the inverse matrix from the left or from the right of matrix
because we can multiply the inverse matrix from the left or from the right of matrix
![]() and we still get the identity matrix. This property is only true for a square matrix
and we still get the identity matrix. This property is only true for a square matrix
![]() .
.
For a rectangular matrix
![]() , we may have
generalized left inverse
or
left inverse
for short when we multiply the inverse from the left to get identity matrix
, we may have
generalized left inverse
or
left inverse
for short when we multiply the inverse from the left to get identity matrix
![]() . Similarly, we may have
generalized right inverse
or
right inverse
for short when we multiply the inverse from the right to get identity matrix
. Similarly, we may have
generalized right inverse
or
right inverse
for short when we multiply the inverse from the right to get identity matrix
![]() . In general, left inverse is not equal to the right inverse.
. In general, left inverse is not equal to the right inverse.
Generalized inverse of a rectangular matrix is connected with solving of system linear equations
![]() . The solution to normal equation is
. The solution to normal equation is
![]() which is equal to
which is equal to
![]() . The term
. The term
![]() is often called as
generalized left inverse
. Still another pseudo inverse can also be obtained by multiplying the transpose matrix from the right and this is called
generalized right inverse
is often called as
generalized left inverse
. Still another pseudo inverse can also be obtained by multiplying the transpose matrix from the right and this is called
generalized right inverse
![]() .
.
Moore-Penrose Inverse
It is possible to obtain unique generalized matrix. To distinguish unique generalized inverse from other non-unique generalized inverses
![]() , we use symbol
, we use symbol
![]() . The unique generalized inverse is called Moore Penrose inverse. It is defined using 4 conditions:
. The unique generalized inverse is called Moore Penrose inverse. It is defined using 4 conditions:
1.
![]()
2.
![]()
3.
![]()
4.
![]()
The first condition
![]() is the definition of generalized inverse. Together with the first condition, the second condition indicates the generalized inverse is reflexive (
is the definition of generalized inverse. Together with the first condition, the second condition indicates the generalized inverse is reflexive (
![]() ). Together with the first condition, the third condition indicates the generalized inverse is the least square solution that minimizes the norm of error
). Together with the first condition, the third condition indicates the generalized inverse is the least square solution that minimizes the norm of error
![]() . The four conditions above make the generalized inverse unique.
. The four conditions above make the generalized inverse unique.
Moore-Penrose inverse can be obtained through
Singular Value Decomposition
(SVD):
![]() such that
such that
![]() .
.
Given a rectangular matrix, the interactive program below produces Moore-Penrose generalized inverse. The Random Example button will generate random matrix. Additionally, the output also include several matrices to let you test the 4 Moore Penrose conditions (
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() ,
,
![]() ) and generalized left inverse or right inverse or matrix inverse depending on the input matrix size. The results can be shown in either rational format or decimal format. The rational output is an approximation of the decimal format.
) and generalized left inverse or right inverse or matrix inverse depending on the input matrix size. The results can be shown in either rational format or decimal format. The rational output is an approximation of the decimal format.
Yes, this program is a free educational program!! Please don't forget to tell your friends and teacher about this awesome program!
Properties
Some important properties of matrix generalized inverse are
-
The transpose of the left inverse of
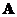 is the right inverse
is the right inverse
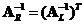 . Similarly, the transpose of the right inverse of
. Similarly, the transpose of the right inverse of
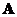 is the left inverse
is the left inverse
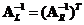 .
.
-
A matrix
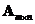 has a left inverse
has a left inverse
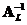 if and only if its rank equals its number of columns and the number of rows is more than the number of column
if and only if its rank equals its number of columns and the number of rows is more than the number of column
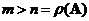 . In this case
. In this case
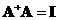 .
.
-
A matrix
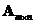 has a right inverse
has a right inverse
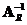 if and only if its rank equals its number of rows and the number of rows is less than the number of columns
if and only if its rank equals its number of rows and the number of rows is less than the number of columns
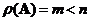 . In this case
. In this case
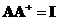 .
.
-
Moore Penrose inverse is equal to left inverse
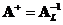 when
when
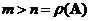 and equal to right inverse
and equal to right inverse
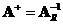 when
when
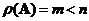 . Moore Penrose inverse is equal to matrix inverse
. Moore Penrose inverse is equal to matrix inverse
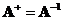 when
when
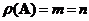 .
.
See also: Solving System of Linear Equations , Singular Value Decomposition , matrix Inverse , matrix transpose
Rate this tutorial or give your comments about this tutorial
