Distance Tutorial: Normalized rank
Rating and Rank are ordinal variables that can be transformed into quantitative variables through normalization. Once the ranks are normalized, the distance can be computed as quantitative variables.
To determine distance between two objects represented by ordinal variables, we need to transform the ordinal scale into ratio scale by performing the following steps:
Convert the ordinal value into rank (r = 1 to
![]() )
)
Normalized the rank into standardized value of zero to one [0,1] by
![]()
Distance can be calculated by treating the ordinal value as quantitative variables (i.e. Euclidean distance , city block distance , Chebyshev distance , Minkowski Distance , Canberra distance , Angular separation , coefficient correlation )
This approach has strong assumption that rank can be normalized as a quantitative variable . To deal with pure rank data, you may use other distance such as Spearman Distance , Kendall Distanc e, Cayley Distance , and Hamming Distance for ordinal variables , Ulam Distance , and Chebyshev /Maximum Distance for ordinal variable.
Example:
We have questionnaire to ask level of satisfaction in term of safety, comfortable, convenient and proximity for two locations of park: park A and park B. Each level of satisfaction has 5 values: -2 = Very dissatisfied, - 1 = dissatisfied, 0 = indifference, 1 = satisfied, 2 = Very satisfied. Suppose the answers of respondent is as the following
|
|
Safety |
Comfortable |
Convenient |
Proximity |
|
Park A |
-2 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
|
Park B |
0 |
1 |
-1 |
1 |
We want to measure dissimilarity of park A and B according to the respondent answer
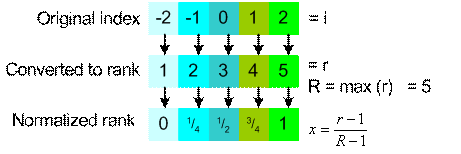
First, we transform the ordinal scale into ratio scale. Original index (i = -2 to 2) is ordered and converted into rank (r = 1 to 5). The highest rank is R = 5. Then we normalized the rank into value [0, 1]. For instance in the position 2, we have i = -1, converted to rank become r = 2. Normalized rank is
![]() . Using the normalized rank as new values, we have coordinates of Park A =
. Using the normalized rank as new values, we have coordinates of Park A =
![]() and park B =
and park B =
![]() . The Euclidean distance between park A and park B is
. The Euclidean distance between park A and park B is
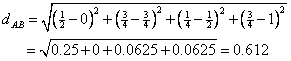
Preferable reference for this tutorial is
Teknomo, Kardi (2015) Similarity Measurement. http:\people.revoledu.comkardi tutorialSimilarity

