Orthogonal Matrix
A matrix is orthogonal if the
transpose
is equal to its
inverse
, that is
![]() .
.
Since computing matrix inverse is rather difficult while computing matrix transpose is straightforward, orthogonal matrix make difficult operation easier. Orthogonal matrix is important in many applications because of its properties.
Example:
Is matrix
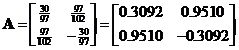 an orthogonal matrix?
an orthogonal matrix?
Answer:
To test whether a matrix is an orthogonal matrix, we multiply the matrix to its transpose. If the result is an identity matrix, then the input matrix is an orthogonal matrix.

Thus, matrix
![]() is an orthogonal matrix.
is an orthogonal matrix.
To create random orthogonal matrix as in the interactive program below, I created random symmetric matrix and compute the modal matrix from concatenation of the Eigen vectors .
The interactive program below is designed to answers the question whether the given input matrix is an orthogonal matrix. When you click Random Example button, it will create random input matrix to provide you with many examples of both orthogonal and non-orthogonal matrices. You can also try to input your own matrix to test whether it is an orthogonal matrix or not.
Properties
Some important properties of orthogonal matrix are
- Orthogonal matrix is always a square matrix
-
If
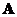 is an orthogonal matrix order
is an orthogonal matrix order
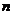 with real entries then
with real entries then
-
The
inner product
of two row vectors or two column vectors of matrix
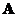 is zero
is zero
-
The row vector and the column vector of matrix
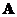 is
orthonormal
(the Euclidean
vector norm
is one)
is
orthonormal
(the Euclidean
vector norm
is one)
-
The
transpose
matrix
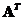 is also an orthogonal matrix
is also an orthogonal matrix
-
The
inverse
matrix
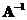 is also an orthogonal matrix
is also an orthogonal matrix
-
The
product
to its transpose is
identity matrix
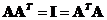
-
The absolute magnitude the
determinant
is one, that is
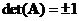
-
The
eigenvectors
of
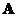 are real and orthogonal
are real and orthogonal
-
The
eigenvalues
of
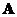 are equal to +1 or -1 (note the theoretical of eigenvalue and eigenvectors of orthogonal matrix is sometimes difficult to obtain numerically due to round off error).
are equal to +1 or -1 (note the theoretical of eigenvalue and eigenvectors of orthogonal matrix is sometimes difficult to obtain numerically due to round off error).
-
If
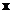 and
and
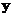 are vector of
are vector of
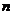 dimensions, then
dimensions, then
-
Inner product
with orthogonal matrix is preserved
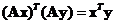
-
Euclidean norm is preserved
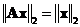
-
Inner product
with orthogonal matrix is preserved
-
The
inner product
of two row vectors or two column vectors of matrix
-
For any square matrix
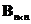 , there exist a unitary matrix
, there exist a unitary matrix
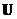 such that matrix
such that matrix
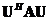 is upper triangular (Schurs theorem).
is upper triangular (Schurs theorem).
- Unitary matrix is generalization of orthogonal matrix with entries of complex numbers
- Both Hermitian and Unitary matrix (including symmetric and orthogonal matrix) are called normal matrix because the eigen vectors form orthonormal set.
See also : Singular Value Decomposition , orthogonal vector , spectral decomposition
Rate this tutorial or give your comments about this tutorial
